The dark web is part of the hidden web, which comprises non-indexed websites that are mostly used for illegal and illicit activity. If you have heard your peers or colleagues throw this term around and are wondering, “What is the dark web?,” this guide is for you.
We’ll discuss how the dark web works and highlight its dangers. However, though the dark web is synonymous with nefarious activity, it does have some benefits. We’ll also shed light on some of the legal uses of the dark web and show you how to access it securely in a detailed step-by-step guide.
What Is the Dark Web?
The dark web is part of the deep web and is hosted on darknets and encrypted networks like Tor, Freenet and Riffle. It comprises websites, resources and services that aren’t indexed by regular web crawlers. The websites are hidden in layers of encryptions and use dot (.) onion domains, which is why they are called onion sites.
Dark web encryption allows website owners and users to stay completely anonymous during their engagement. The high level of anonymity is the main reason the dark web is replete with illegal activity, from drug dealing and arms trafficking to the sharing of exploitative content and stolen login credentials.
Deep Web vs Dark Web vs Surface Web
The internet is divided into two main parts: the open and the hidden web. The open web (also known as the surface web) is the part of the internet that’s easily accessible to all users. Web crawlers index websites and services on the surface web, which are accessible via regular browsers.
The hidden web (also known as the deep web or deep net) is the largest part of the internet. It comprises websites that aren’t easily accessible mainly because they are non-indexed, password-protected or paywalled. The dark web is a small subset of the deep web comprising purely non-indexed websites and services.
| Attributes: | Surface Web | Deep Web | Dark Web |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scope | Indexed websites (About 4% of total internet) |
Indexed but paywalled or password-protected websites (About 90% of total internet) |
Non-indexed websites (About 5% of total internet) |
| Access | Can be accessed via regular browsers: Google, Bing, Firefox, etc. | Some can be accessed via regular browsers, but others may require anonymizing browsers like TOR | Can only be accessed via anonymizing browsers |
| Security | Secure | Secure | Legal & security risks |
| Application | Provides digital services to the average internet user | Intranets, academic institutions, subscription-based services, internal networks used by corporations | Provides anonymity, facilitates illegal activity and the sale of illegal goods |
| Experience | User-friendly | User-friendly | Not user-friendly |
| Examples | Facebook, Google, blogs, YouTube, Wikipedia, etc. | Internet banking, private forums, internal networks, Hidden Wiki, medical records, research papers, etc. | Non-indexed websites, Silk Road, SecureDrop, AHMIA, etc. |
How to Access the Dark Web or Deep Web Using Tor
If you’re intrigued and want a firsthand experience, follow this guide to learn how to access the deep web with an anonymizing browser. We’ll use the Tor browser for this guide, but any other browser that supports the Tor protocol will do.
We also recommend using a virtual private network (VPN) such as ExpressVPN — the best dark web VPN — to add an extra layer of protection. You can read our ExpressVPN review for more information, or try it out yourself using the 30-day money-back guarantee.
Anonymizing browsers are banned in some countries like China and Russia. Moreover, given the nefarious nature of the dark web, some government agencies may set up Tor gateways to monitor what’s happening on the dark web.
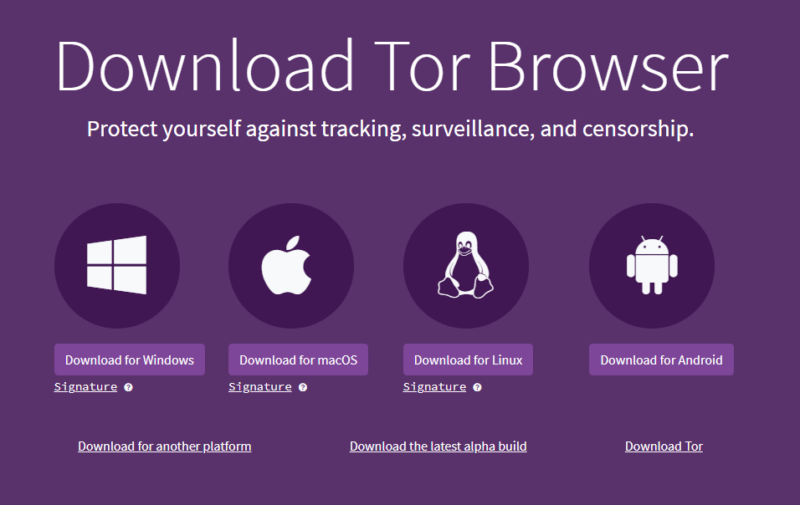
- Download and Install a Browser that Supports Tor
Go to the Tor Project’s website and download the Tor browser for a Windows, Mac, Linux or Android device. Double-click the installation file to install the browser on your device. If Tor and other anonymizing browsers are blocked in your country, connect to a VPN to circumvent censorship.
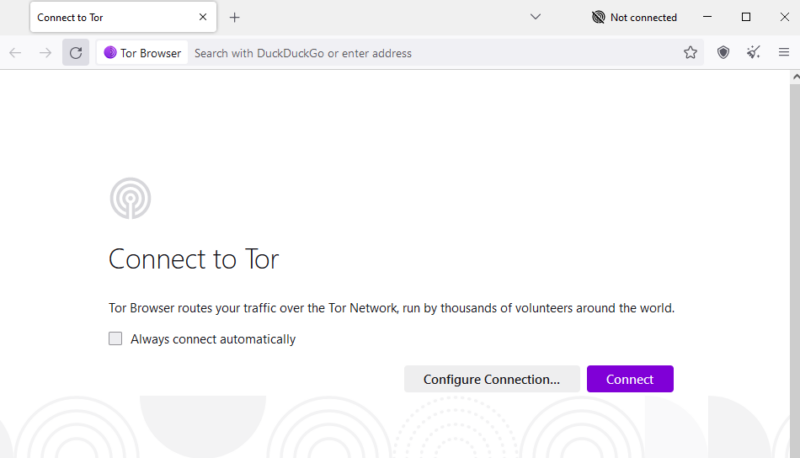
- Connect to the Tor Network
When you launch the Tor browser for the first time, you’ll have the option to set up the Tor network. Click “connect” to ensure the browser routes your traffic over a Tor network.
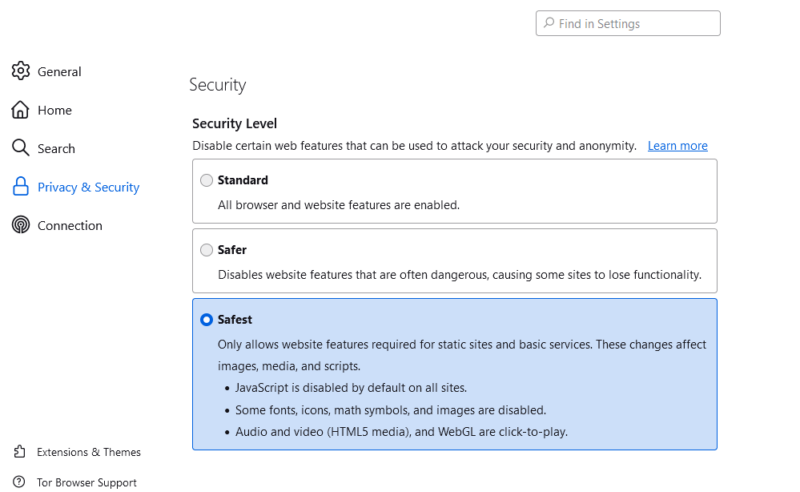
- Configure Security and Privacy Features
Configure the browser’s security and privacy settings to the highest levels. At the top right, open the browser’s settings and select “privacy and security.” Configure the browser privacy and permissions to your liking, scroll down to the “security” section and set the security level to “safest” mode.
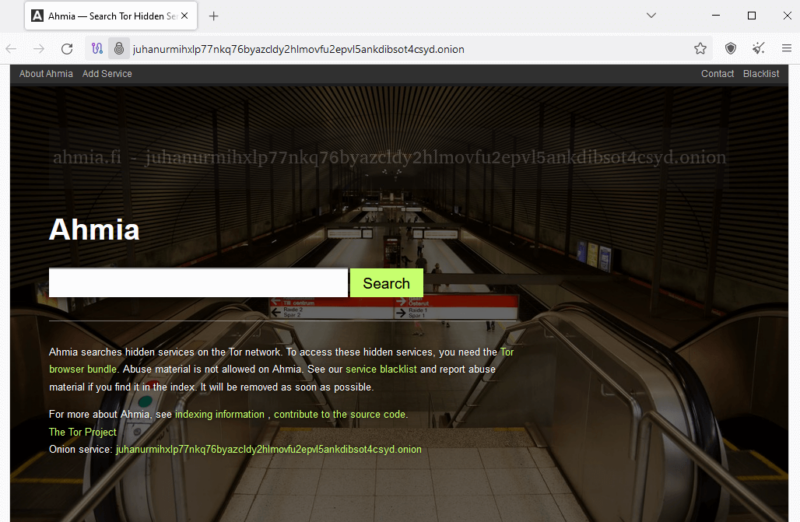
- Browse the Dark Web
Before you access an onion site, connect to a VPN to add an extra layer of anonymity to your traffic. Read the “Is the Dark Web Dangerous?” section of this article to understand why a VPN is indispensable. Type the dark web address into the search bar and press “enter.”
Understanding How the Deep Web Works
To better understand how the dark and the deep web work, you must first understand how the open web operates. Web crawlers run the regular internet, scouring the web to discover newly published websites or pages in a process called crawling.
Discovered pages are indexed in an extensive database and ranked based on numerous factors. When you search a term (or query) in a web browser, the search engine combs through the database to find relevant results and serves them up on SERPs.
In the deep net, web crawlers are blocked from accessing web pages to gather information for indexing, so the content remains hidden. Some content and services on the deep web are indexed by search engines, but paywalls or password protection prevent access. Content and services on the deep web are accessible through a regular browser.
Examples of deep web content include blog posts that aren’t yet published, web pages undergoing a redesign, email inboxes, financial data, research papers, social security databases, legal files, private forums, medical records, pay-to-access services and social media.
Dark web sites are hidden by non-indexing, making them completely anonymous. As a result, they are not accessible via regular browsers. You’ll need a purpose-built browser that uses The Onion Router (TOR) to access dark web content. Because of their anonymity, dark web sites are breeding grounds for illegal activity and transactions.
Is It Legal to Access the Deep Web?
Yes, accessing the deep web and dark web is perfectly legal. After all, some websites on the deep web are like those on the open internet, except that they are hidden behind a paywall or protected via passwords to limit access.
There are no laws restricting access to websites on the dark web. However, using the dark web for illegal activity can be a criminal offense.
Benefits of Using the Deep Web
In this section, we’ll look at the benefits of the deep web (an umbrella term that includes the dark web). The deep web has been so mythologized that using it seems suspect on the surface. However, this part of the internet has numerous benefits, including:
- Abundance of information: Since the deep web is the largest part of the internet, it has far more information than the open web. In addition to millions of resourceful pages, you’ll find database entries, TV shows and stories that are ordinarily not available on the surface web.
- Educational materials: The deep web is a treasure trove of scientific findings and literature that haven’t been made public on the surface web. This makes it a great space for students, teachers and researchers. You’ll also find hacking tutorials and cybercrime courses.
- Privacy and anonymity: The deep web offers more privacy than the surface web. It uses onion routing technology that provides multiple layers of encryption to guard information and data in transit. This protects users from the surveillance and tracking often associated with the surface web.
- Freedom of expression: Freedom of speech is a direct benefit of anonymity. Deep web tools route traffic through many nodes, making it difficult to single out a user or trace their browsing history. The layers of encryption boost anonymity, enabling users to share any information without fear of retribution or persecution.
Is the Dark Web Dangerous?
The dark web is dangerous in some cases and safe in others. Let’s explain. One study found that only 6.7% of Tor anonymity network daily users — a cohort that comprises mostly dark web users — connect to onion sites used for illicit activity. This essentially means that over 93% of Tor daily users use the dark web for legitimate reasons.
Regardless of what brings you to the dark web, you should be aware of the dangers emanating from the limitations of the Tor network.
The Danger of Tor Network
The Tor network’s principal benefit is that it routes your traffic through numerous servers, wrapping it in several layers of encryption. This makes it difficult for interlopers to monitor the traffic or trace any legal or criminal activity back to you.
Behind the facade of this benefit lies an inherent risk. Volunteers worldwide operate the proxy servers (or Tor nodes). You can never be sure of the motive of the person operating the node that your traffic is routed through.
Though most volunteers mean well, others are malicious actors and surveillance agencies. The worst part of the network is that you don’t have control over the nodes your traffic is routed through.
If your incoming traffic passes through a node run by cybercriminals, they could inject malware into the response code. If your device is unprotected, you could be a victim of malware or a hacking attack.
Danger of Surveillance Agencies

vulnerabilities that authorities and hackers use to track users.
The Tor network is made up of three types of nodes. The entry node is the first server in the Tor chain, the relay node is the middle node and the exit node is the last server in the network.
There’s evidence that law enforcement agencies in freer countries operate many exit nodes for monitoring and surveillance purposes. This is because Tor traffic is usually unencrypted when it passes through the exit node.
Law enforcement officials can exploit that weakness using “Tor-exit-node” monitoring techniques to expose users’ IP addresses and potentially trace activity back to the original users. If you’re on the dark web to engage in illegal activity and your traffic passes through a compromised exit node, your secrets can be exposed.
Is the Dark Web Illegal?
No, the dark web isn’t illegal, but what you do while in the underbelly of the internet matters. A lot of illegal activity takes place on the dark web, and engaging in any of that activity can be a criminal offense.
Keep in mind that in some regions like China and Russia, it’s illegal to use anonymizers. Tor would probably be considered an anonymizer. If you’re in a restrictive country, you’ll be crossing the red line and authorities could be at your heels. The silver lining is that no one has been arrested or prosecuted for using an anonymizing browser.
What Can You Buy on the Dark Web?
Virtually anything you can buy on the surface or clear web you can also find on the dark web. Books, video games, apparel and rare collectibles are some of the legal items you can buy on dark web commerce sites.
However, the vast majority of items found on dark web marketplaces are illegal or illicit. The most prevalent illicit products are pharmaceutical and recreational drugs, followed by stolen data, online bank account credentials and credit card numbers. Other illegal items include:
- Firearms
- Counterfeit currency
- Pornographic content
- Toxic chemicals
- Hacked databases
- Fake passports and driver’s license numbers
- Hacked Netflix accounts from data breaches
- Personal identifiable information (PII)
In addition, you can buy media, software, malware and malware-as-a-service (MaaS) products, including:
- Hacking, social engineering and cracking tutorials
- Hacked and pirated software
- Ransomware and botnets
- Spam
- Crypto miners and other tools used for cryptojacking
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS) and phishing email attack tools
Dark Web Tools & Services
Accessing the dark web is surprisingly easy and safe if you have the right tools in your technology stack. Here are some of the tools and services you need:
Dark Web Browsers
To access the dark web, you need an anonymizing web browser or any browser that supports the Tor network. The Tor Browser is the most popular browser for the dark web, but other popular options exist, like Brave, Comodo Dragon, Epic and SRWare Iron.
Dark Web Search Engines
DuckDuckGo is the best dark web search engine, as it offers an excellent user experience akin to surface web search engines. Its effectiveness in scouring the shadowy depths of the dark web can be likened to what Google does on the surface web.
Beyond DuckDuckGo, other options have failed to keep up with the evolving landscape. These options include Torch, NotEvil, Haystak, Candle and AHMIA. Though these browsers are effective at serving up dark web search results, the experience is reminiscent of browsing the web in the late 1990s.
Dark Web VPN

A VPN encrypts your traffic before it goes into the Tor network. This adds an extra layer of protection to thwart tracking and monitoring in case the traffic passes through a compromised exit node.
If the traffic passes through a Tor exit node run by a law enforcement agency, they will only see the IP address that the VPN assigned, not your real IP. As a result, it would be difficult to locate you or trace the dark web activity back to you. Read our full guide on the best VPN for the dark web.
Dark Web Sites
Dark web websites don’t bear Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN) domains, such as .com. .net, .org or .ai. They use a scramble naming structure that combines a string of letters and numbers to create URLs that are impossible to remember.
For example, The New York Times goes by the unintelligible address https://www.nytimesn7cgmftshazwhfgzm37qxb44r64ytbb2dj3x62d2lljsciiyd.onion/.
Some popular legal dark web websites include:
- Wasabi Wallet
- ProtonMail
- DuckDuckGo
- ProPublica
- ZeroBin
- CIA
- Riseup
- Tor Links
- Comic Book Library
- Keybase
- The Hidden Wiki
- Sci-Hub
- SecureDrop
- Just Another Library
- Archive Today
- AHMIA
- The New York Times
- Impreza Hosting
- BBC Tor Mirror
Final Thoughts
The endless list of illegal activity on the dark web casts a grim picture of this part of the internet and leaves the impression that it’s dangerous. On the contrary, the dark web isn’t inherently risky: It can be a lifeline that gives users in oppressive regimes, whistleblowers, journalists and human rights activists the ability to share sensitive information without the fear of persecution.
Accessing the dark web is easy with the right tools. To be on the safe side, we recommend combining the Tor or onion browser with a secure VPN, such as ExpressVPN. When used in unison, these tools seal the security and privacy vulnerabilities of the Tor network, keeping you anonymous as you roam the streets of the dark web.
Have you visited a dark web site before? Which dark web browser did you use to visit sites on the dark web? Did you use a VPN for extra protection? We’d like to hear about it in the comments section. As always, thanks for reading.
FAQ: The Dark Web
-
Tor is the go-to dark web browser for many users. However, there are other options, like the Epic and Brave browsers.
-
The deep web is good for restricting access to online services such as social media accounts, internet banking or pay-to-access software tools.
-
Yes, parts of the deep web are on Google, but it’s intentionally hidden behind a paywall and passwords or made available as pay-to-access services.
-
Yes, using the Tor browser is safe if the traffic passes through secure nodes. However, the traffic could be intercepted and monitored if it passes through a compromised node, so it’s important to use the Tor browser with a VPN.
-
To access the Tor browser, go to the Tor Project’s website and download and install the browser on your device.
The post What Is the Dark Web & How to Access It Safely in 2024 appeared first on Cloudwards.

