Google Cloud is a cloud computing platform that provides computing resources on demand via the internet. Like other cloud providers, Google Cloud provides the underlying infrastructure and platform for designing and delivering web applications. Google Cloud Platform cost optimization cuts GCP expenses while maximizing service value and preventing cloud waste.
To do this, companies track resource usage, eliminate waste and choose GCP features wisely. Effective optimization practices include rightsizing resources, leveraging committed use discounts and implementing smart tagging strategies.
Tools like Google’s Cost Management suite, Cloudability and CloudHealth provide insights and automate GCP cost management. Optimization reduces cloud spend, improves resource utilization and enhances performance. These strategies can cut cloud costs by 20-30% without sacrificing capabilities.
What Is Google Cloud Cost Optimization?
Google Cloud cost optimization is the process of managing and reducing cloud expenses while maximizing the value derived from GCP services. It involves tracking resource usage, cutting waste and making smart choices with GCP features. This process helps organizations align cloud spending with their needs to prevent overspending and underutilized resources.
GCP cost optimization is necessary because cloud costs can quickly spiral out of control without proper management. As businesses scale their cloud operations, the complexity of resource allocation and pricing models increases. Optimization helps companies avoid unexpected bills, reduce waste and improve their return on cloud investments.
What Does Cloud Cost Optimization Mean?
Cloud cost optimization involves using strategies to manage and cut expenses linked to cloud services while making sure they are as valuable and efficient as possible. This process includes regularly checking and tweaking how cloud resources are used, choosing pricing models that save costs and using tools to keep an eye on spending.
By optimizing cloud costs, organizations make sure their investment in cloud services matches their operational needs and budget limits. Optimization is necessary because cloud environments are dynamic and can scale, which can lead to unpredictable and sometimes high costs if not managed well.
What Are the Best Practices for Google Cloud Cost Optimization?
The best practices for Google Cloud cost optimization include utilizing long-term commitment discounts, implementing cloud monitoring and cloud logging, maximizing resource utilization, leveraging cost management tools and adopting FinOps practices.
What Cloud Resources Contribute to Google Cloud Costs?
The cloud resources that contribute to Google Cloud costs are Compute Engine virtual machines, Kubernetes Engine clusters, Cloud Storage buckets, Cloud SQL databases, networking services like Cloud VPN and Load Balancing, Cloud Functions, Cloud Run services, App Engine applications, BigQuery data processing and Cloud Operations tools.
GCP charges for these resources based on factors such as usage time, data transfer, storage capacity and processing power. We will now look at how you can optimize these resources to reduce cloud costs.
What Are the Best GCP Cost Optimization Tools and Solutions?
The best GCP cost optimization tools and solutions are a combination of native Google Cloud services and third-party platforms designed to help organizations manage and reduce their cloud expenses. Some of the tools we will look at below include Cloud Billing, Recommender and third-party tools such as Flexera.
- Cloud Billing: A GCP native tool that provides detailed cost breakdowns, budgeting features, and cost forecasting capabilities to help manage GCP expenses.
- Recommender: A built-in GCP service that offers personalized recommendations for optimizing resource usage and reducing costs across various GCP services.
- Cost Management: A comprehensive suite of GCP tools, including Breakdown, Reports and Budgets & Alerts, enabling detailed cost analysis and proactive spend management.
- Cloudability: A third-party platform offering advanced methods for allocating costs, rightsizing recommendations and implementing predictive analytics to optimize GCP spending.
- CloudHealth: Provides multi-cloud cost management features, including GCP cost optimization, with detailed reporting and automation capabilities.
- Flexera: Offers comprehensive cloud cost optimization solutions, including resource rightsizing, reserved instance management and budget tracking for GCP.
- ParkMyCloud: Specializes in automated scheduling of compute resources to reduce costs during off-hours — particularly effective for non-production environments.
- Densify: Uses machine learning to analyze cloud usage patterns and provide detailed rightsizing recommendations for GCP resources.
- Apptio Cloudability: Provides FinOps solutions for GCP, including cost allocation, optimization recommendations and financial reporting.
- Spot.io: Offers tools for optimizing costs through the use of preemptible and spot instances in GCP.
What Are the Benefits of GCP Cost Optimization?
The main benefits of Google Cloud Platform (GCP) cost optimization address both financial and operational aspects of cloud management. By implementing effective cost optimization strategies, organizations can significantly reduce their cloud expenditures, enhance resource utilization, improve financial governance and visibility, and increase scalability and flexibility.
- Reduced cost/billing: Practices such as rightsizing and using preemptible VMs can reduce costs by up to 30-40%.
- Enhanced resource utilization: Continuous adjustments lead to optimal utilization, often increasing efficiency levels.
- Improved financial governance and visibility: Tools like budget alerts and detailed billing reports enhance financial tracking and forecasting.
- Scalability and flexibility: Auto-scaling and flexible pricing adapt to changing needs, preventing overprovisioning and underutilization.
- Increased competitiveness: Savings from optimization can be reinvested in innovation, enhancing competitiveness in the market.
What Is GCP’s Pricing Plan?
GCP’s pricing plan refers to the overall structure and approach that Google Cloud Platform uses to charge customers for its cloud services. Google Cloud Platform’s pricing plan centers on resource consumption. The free option offers limited usage of more than 20 key services, like Compute Engine, Cloud Storage and Cloud Functions, at no cost.
For example, Compute Engine allows only one f1-micro VM instance per month in supported regions, with a maximum of 720 hours per month.
For paid services, costs are primarily driven by compute usage (based on vCPU and memory), storage volume, data processing and network traffic. Specialized services like databases, AI, and machine learning tools have their own pricing structures.
GCP’s billing is granular, often calculated to the second, which ensures customers pay for only the resources they actually use. It also provides discounts apart from the free tier, as shown in the table below.
| Discount Type | Description | Potential Savings |
|---|---|---|
| Sustained use | Automatic discounts for running compute instances for a significant portion of the billing month | Up to 30% |
| Committed use | Discounts for committing to using a certain number of resources for 1 or 3 years | Up to 57% for most resources |
| Preemptible VMs | Low-cost, short-lived compute instances suitable for batch jobs and fault-tolerant workloads | Up to 60%-91% compared to regular instances |
| Spot VMs | Similar to preemptible VMs but with flexible pricing based on supply and demand | Up to 91% compared to regular instances |
| Custom machine types | Ability to create VM instances with custom CPU and memory configurations | Varies, but can be more cost-effective than predefined machine types |
| Inferred instance types | Automatic recommendations for cost-effective machine types based on usage patterns | Varies based on specific recommendations |
| Volume discounts | Automatic discounts for high-volume usage of certain services (e.g., cloud storage) | Varies based on usage volume |
Does GCP Offer Free Tier Usage?
Yes, Google Cloud Platform (GCP) offers a free tier. This includes limited access to many of its services and resources at no cost, such as Compute Engine, Cloud Storage and BigQuery, which is ideal for learning, experimenting and building applications on GCP without an initial investment.
What Are the Different GCP Pricing Models?
GCP offers four pricing models: free, subscription-based, usage-based and combined pricing.
- Free model: GCP offers a free tier that includes always-free usage limits on popular services, plus a 90-day trial with a $300 credit. This allows users to explore and test GCP services at no cost.
- Subscription-based model: This model involves paying a fixed fee for a predetermined set of resources or services for a specific period of time. It’s often used for committed use discounts, where customers commit to using certain resources for one or three years in exchange for significant discounts.
- Usage-based model: Also known as pay-as-you-go, this model charges customers based on their actual resource consumption. Billing is often calculated down to the second, ensuring customers only pay for what they use.
- Combined pricing model: This approach mixes elements of the other models. For example, a customer might use the free tier for some services, have committed use discounts for predictable workloads and rely on pay-as-you-go for variable resource needs.
How to Use the GCP Pricing Calculator for Cost Estimation
GCP has a pricing calculator that allows you to estimate the cost of your cloud infrastructure by entering your forecasted usage. Follow the steps below to use the GCP pricing calculator to generate a cost estimate:
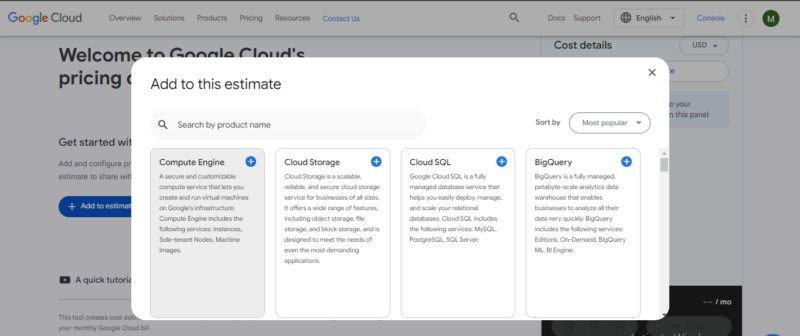
- Access the calculator and choose the service you want to estimate
Go to the Google Cloud pricing calculator website. The example below is for Compute Engine.
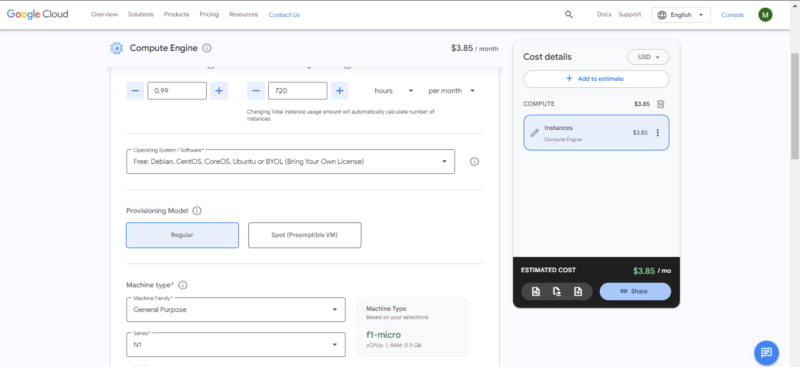
- Configure Your Instance
Choose the region and instance type, specify the number of instances and the operating system, and enter the estimated running hours per month. Note that in free-tier mode you can have only 720 hours per month and one f1-micro machine type. Don’t forget to include any necessary extra storage or anticipated network usage.
{“@context”:”https:\/\/schema.org”,”@type”:”HowTo”,”name”:”Steps”,”description”:”These step-by-step instructions show how to use the GCP pricing calculator for cost estimation.”,”totalTime”:”P00D02M00S”,”supply”:0,”tool”:0,”url”:”https:\/\/www.cloudwards.net\/google-cloud-cost-optimization\/#steps”,”image”:{“@type”:”ImageObject”,”inLanguage”:”en-US”,”url”:”https:\/\/www.cloudwards.net\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/08\/Google-Cloud-Cost-Optimization.png”},”step”:[{“@type”:”HowToStep”,”name”:”Access the calculator and choose the service you want to estimate”,”position”:1,”url”:”https:\/\/www.cloudwards.net\/google-cloud-cost-optimization\/#access-the-calculator-and-choose-the-service-you-want-to-estimate”,”itemListElement”:{“@type”:”HowToDirection”,”text”:”Go to the Google Cloud pricing calculator website. The example below is for Compute Engine.\n”},”image”:{“@type”:”ImageObject”,”inLanguage”:”en-US”,”url”:”https:\/\/www.cloudwards.net\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/08\/choose-the-service.png”}},{“@type”:”HowToStep”,”name”:”Configure Your Instance”,”position”:2,”url”:”https:\/\/www.cloudwards.net\/google-cloud-cost-optimization\/#configure-your-instance”,”itemListElement”:{“@type”:”HowToDirection”,”text”:”Choose the region and instance type, specify the number of instances and the operating system, and enter the estimated running hours per month. Note that in free-tier mode you can have only 720 hours per month and one f1-micro machine type. Don’t forget to include any necessary extra storage or anticipated network usage.\n”},”image”:{“@type”:”ImageObject”,”inLanguage”:”en-US”,”url”:”https:\/\/www.cloudwards.net\/wp-content\/uploads\/2024\/08\/configure-instance.png”}}]}
Check the total estimate and modify configurations as needed for budget or performance. You can export the estimate to a CSV file or share it via a direct link if you need to discuss it with team members or keep it for your records.
What Is the Main Difference Between GCP and AWS Pricing Plans?
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and Amazon Web Services (AWS) have distinct approaches to pricing their cloud services. The table below highlights the key differences in their pricing plans:
| Feature | Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Amazon Web Services (AWS) |
|---|---|---|
| Billing increment | Per-second billing for most services | Per-second billing for some services, per-hour for others |
| Sustained use discounts | Automatic discounts for sustained use | Automatic discounts for sustained use |
| Committed use discounts | 1-year and 3-year options | 1-year and 3-year options (called Reserved Instances) |
| Free tier | $300 credit for 90 days and always-free tier | 12-month free tier for many services |
| Pricing model | Generally simpler, more straightforward | More complex, with many pricing options |
| Instance flexibility | Custom machine types available | Fixed instance types with some flexibility |
| Pricing calculator | Simple and user-friendly | Comprehensive but can be complex |
Between GCP and AWS, which one is cheaper often depends on the specific use case and workload. GCP tends to be more cost-effective for variable or unpredictable workloads due to its per-second billing and automatic sustained use discounts. AWS can be more economical for steady, predictable workloads when using Reserved Instances.
For startups and small projects, GCP’s free tier might be more generous initially, while AWS’ 12-month free tier could be beneficial for longer-term exploration. Ultimately, a detailed cost analysis based on specific requirements is necessary to determine which platform is more cost-effective for a particular use case.
What Is the Main Difference Between GCP and Azure Pricing Plans?
Google Cloud Platform (GCP) and Microsoft Azure offer unique pricing models tailored to their strengths and target markets. The table below compares their key pricing features:
| Feature | Google Cloud Platform (GCP) | Microsoft Azure |
|---|---|---|
| Billing increment | Per-second billing for most services | Per-second billing for many services |
| Sustained use discounts | Automatic discounts for sustained use | No automatic sustained use discounts |
| Committed use discounts | 1-year and 3-year options | 1-year and 3-year options (called Reserved Instances) |
| Free tier | $300 credit for 90 days and always-free tier | $200 credit for 30 days and always-free services |
| Pricing model | Generally simpler, more straightforward | Complex, with many options and licensing considerations |
| Instance flexibility | Custom machine types available | Fixed VM sizes with some flexibility |
| Hybrid cloud support | Less emphasis on hybrid solutions | Strong focus on hybrid cloud with Azure Stack |
| Licensing benefits | Limited | Significant for existing Microsoft customers |
Azure has stronger integration with Microsoft’s ecosystem and an emphasis on hybrid cloud solutions, while GCP offers a simpler pricing structure with automatic discounts. Azure tends to be more cost-effective for organizations already invested in Microsoft technologies, whereas GCP’s pricing model can be better for cloud-native applications and variable workloads.
Final Thoughts
Managing cloud costs is an ongoing process. Remember, the key to effective cloud cost management lies in continual monitoring, regular adjustments and leveraging the right mix of services and discount options for your specific needs.
How do these cost optimization strategies align with your business goals? Are there specific challenges you face in managing cloud expenses? Please feel free to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Thank you for reading.
FAQ: Google Cloud Cost Management
-
Optimize resource allocation, use preemptible VMs, leverage sustained use discounts, implement auto-scaling and utilize GCP cost management tools like Cloud Monitoring and Billing reports.
-
It depends on the specific use case. GCP can be cheaper for variable workloads due to per-second billing and automatic discounts. AWS may be more cost-effective for steady, predictable workloads using reserved instances.
-
Rightsize resources, use committed use discounts for predictable workloads, clean up unused resources, optimize network usage, use preemptible VMs where possible, and regularly review and act on GCP’s cost optimization recommendations.
{“@context”:”https:\/\/schema.org”,”@type”:”FAQPage”,”mainEntity”:[{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”How to Optimize Google Cloud Costs?\u00a0″,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
Optimize resource allocation, use preemptible VMs, leverage sustained use discounts, implement auto-scaling and utilize GCP cost management tools like Cloud Monitoring and Billing reports.\n”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”Is GCP Cheaper Than AWS?”,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
It depends on the specific use case. GCP can be cheaper for variable workloads due to per-second billing and automatic discounts. AWS may be more cost-effective for steady, predictable workloads using reserved instances.\n”}},{“@type”:”Question”,”name”:”How to Reduce the Google Cloud Bill?\u00a0″,”acceptedAnswer”:{“@type”:”Answer”,”text”:”
Rightsize resources, use committed use discounts for predictable workloads, clean up unused resources, optimize network usage, use preemptible VMs where possible, and regularly review and act on GCP’s cost optimization recommendations.\n”}}]}
The post Google Cloud Platform Cost Optimization: Definition, Best Practices, Tools and Benefits appeared first on Cloudwards.