In the ever-changing world of data-driven decision-making and regulatory requirements, ensuring compliance with data governance standards has become an indispensable aspect of modern organizations. Data compliance refers to the adherence to legal, ethical, and industry-specific regulations that dictate how data should be collected, stored, processed, and shared. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in severe consequences, such as hefty fines, reputational damage, and loss of customer trust.
To navigate these challenges successfully, businesses are increasingly turning to data version control, a crucial technique that ensures data integrity, traceability, and accountability. In this article, we will delve into the concepts of data version control and data compliance, and explore their implementation to safeguard an organization’s valuable data assets.
Understanding Data Version Control
Data version control is a systematic approach to managing changes and updates to data over time. Much like version control in software development helps you track versions of your software, data version control helps you track, document, and maintain data transformations with precision and transparency.
This process involves capturing the history of data modifications, attributing them to specific individuals, and enabling easy retrieval of previous states. Data version control is especially relevant in scenarios where multiple data contributors are involved, such as organizations where data scientists, analysts, and engineers collaboratively work on datasets.
How Data Version Control Works
At its core, data version control relies on the principle of creating snapshots of data at different points in time. Each snapshot represents a version of the dataset, capturing its state and content at that specific moment. When changes are made to the data, a new snapshot is created, documenting the modifications made. These snapshots are organized in chronological order, forming a timeline of the dataset’s evolution.
To facilitate data version control, organizations often adopt specialized tools and platforms designed explicitly for this purpose. These tools offer features like data version tracking, access control, and collaboration capabilities. Git, a popular version control system in software development, has been extended to support data version control as well, making it a great option for managing data transformations.
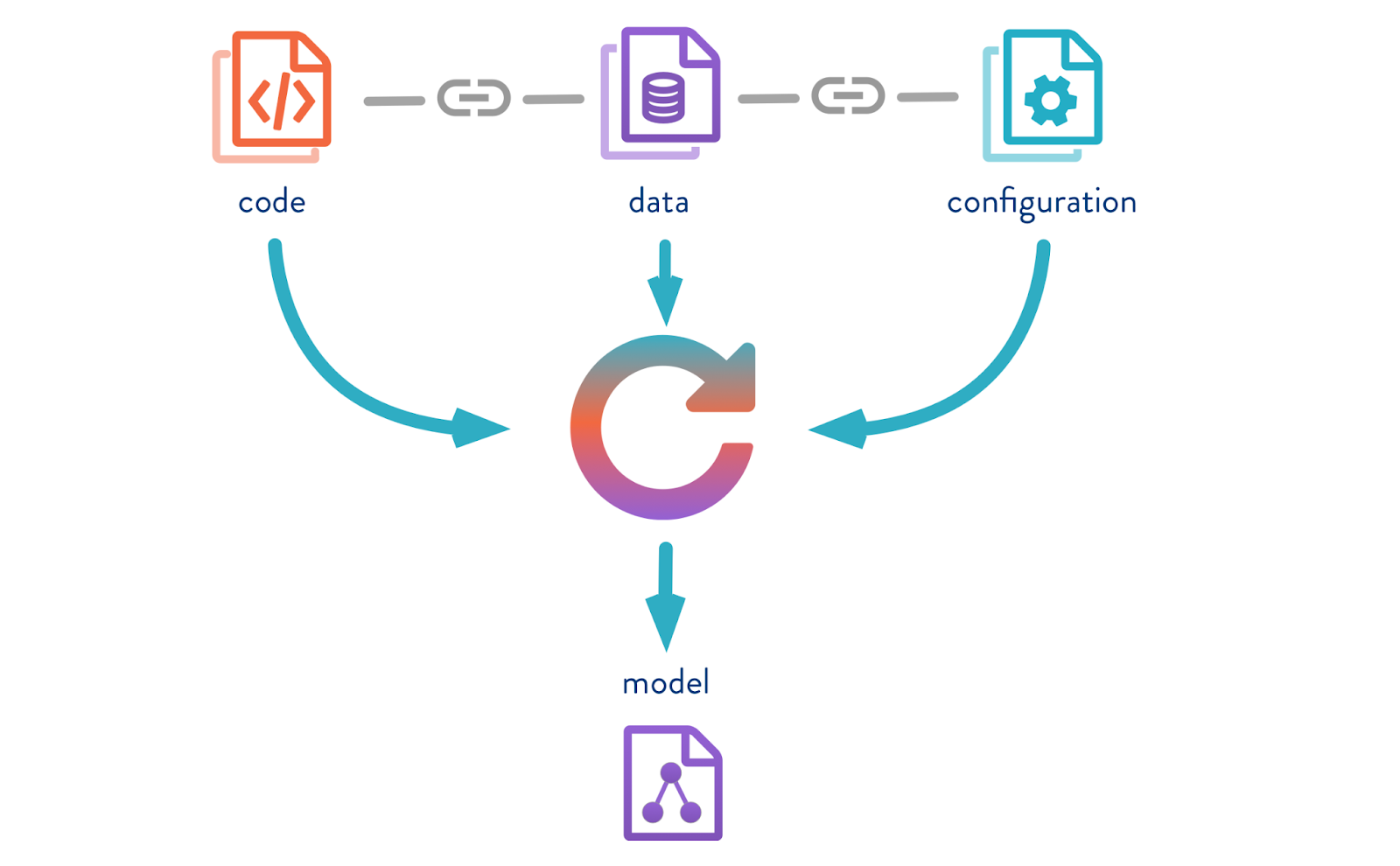
Why Data Version Control is Important
Implementing data version control offers several significant advantages to organizations:
- Data Integrity: With data version control, organizations can ensure that changes to critical datasets are well-documented and traceable. This reduces the risk of accidental data corruption and helps maintain data quality and accuracy.
- Collaboration and Accountability: Data version control allows multiple teams and individuals to collaborate on data projects efficiently. Each data transformation is attributed to a specific user, making it easier to track who made changes and when.
- Reproducibility: Having access to historical versions of data enables the replication of analyses and experiments conducted in the past. This reproducibility is crucial for data validation and regulatory audits.
- Error Recovery: In the event of an error or unintended data transformation, data version control provides the ability to revert to a previous, known-good state, mitigating potential data loss.
- Facilitates Compliance: By keeping a well-documented history of data changes, organizations can demonstrate compliance with various regulations and internal data governance policies.

The Significance of Data Compliance
Data compliance is a multifaceted concept that encompasses adherence to legal, ethical, and industry-specific data regulations. The primary objective of data compliance is to ensure that data is handled responsibly, transparently, and securely. There are several key aspects of data compliance that organizations must consider:
Legal Regulations
Various countries and regions have enacted data protection laws to safeguard the privacy and security of individuals’ personal information. The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States are prominent examples of such regulations. Organizations collecting and processing personal data must comply with these laws, which often require obtaining explicit consent, providing data subjects with access to their information, and ensuring secure data storage and transmission.
Industry Standards
Many industries, such as finance, healthcare, and telecommunications, have established specific data compliance standards to address sector-specific challenges. For instance, the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the healthcare industry mandates strict controls on the handling of patient health information.
Data Governance Policies
Apart from external regulations, organizations often create their own internal data governance policies. These policies outline the guidelines and best practices for data management within the organization. Data compliance efforts should align with these policies to maintain consistency and integrity across all data-related processes.
Risk Management
Data compliance is closely linked to risk management. Non-compliance poses significant risks to an organization, including legal liabilities, financial penalties, and damage to reputation. Implementing robust data compliance measures reduces these risks and ensures long-term sustainability.
The Intersection of Data Version Control and Data Compliance
Data version control plays a crucial role in ensuring data compliance across different regulatory frameworks. By combining the capabilities of data version control with data compliance strategies, organizations can achieve a comprehensive approach to data management that addresses key compliance challenges:
Auditability and Traceability
Data version control provides a detailed history of data changes, including who made the changes and when. This audit trail enhances transparency and traceability, which are essential aspects of data compliance. In the event of a regulatory audit, organizations can provide evidence of compliance by presenting the data version history.
Data Minimization and Retention Policies
Many data compliance regulations emphasize the principle of data minimization, which means collecting and retaining only the necessary data for a specific purpose. Data version control helps enforce data minimization by allowing organizations to monitor changes and identify unnecessary additions to datasets.
Access Control and Data Security
Data compliance often requires strict access controls to protect sensitive information from unauthorized access. Data version control platforms can integrate with existing access control mechanisms, ensuring that only authorized individuals have the right to modify certain datasets.
Data Validation and Quality Assurance
Data compliance efforts rely on accurate and reliable data. Data version control facilitates data validation and quality assurance by enabling data scientists and analysts to compare different versions of the data and validate its accuracy over time.
Change Management
Regulatory changes and updates are common, and organizations must adapt to these changes to maintain compliance. Data version control aids in change management by allowing organizations to implement data updates in a controlled and documented manner.
Conclusion
In the digital era, data compliance has become a fundamental aspect of organizational success. Adhering to legal regulations, industry standards, and internal data governance policies is crucial for maintaining data integrity, protecting customer privacy, and avoiding legal repercussions. Data version control complements data compliance efforts by providing an efficient and transparent approach to managing data changes and facilitating accountability among data contributors.
By adopting data version control practices and leveraging specialized tools, organizations can demonstrate compliance, enhance data integrity, and mitigate risks effectively. The seamless integration of data version control and data compliance paves the way for data-driven organizations to thrive in an increasingly regulated and data-centric world.
The post Implementing Data Version Control to Ensure Compliance appeared first on Datafloq.

